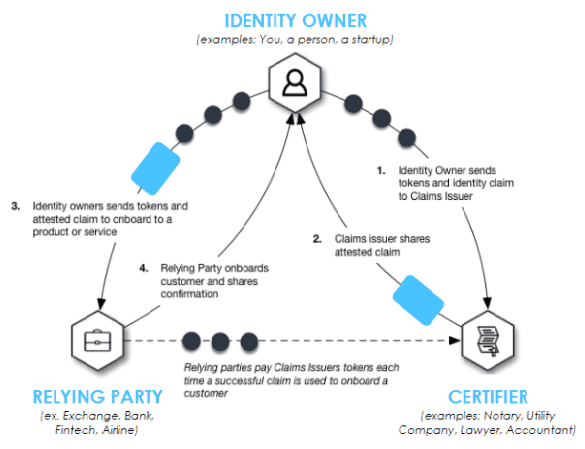
Centralized identity management systems are beset with many challenges that make them prone to various security and administrative complications. The deficiencies of centralized systems For instance, storing sensitive data of individuals in a particular location or server makes storage platform a prime target for hackers and identity thieves. There is also the risk of loss of identity in the case of eventualities like a system crash, or identity mismanagement by insincere administrators who may employ client information for non-permitted uses. Despite advancement and disruption in other domains, the identity systems we rely upon today are currently paper-based, nationally-driven, government identity systems and do not leverage the power of the blockchain. Therefore, transporting such information when needed, sometimes internationally could become cumbersome and time consuming. Vulnerability and losses Besides the inefficiencies encountered in central identity management systems, owners of these identities do not have control over their data and are vulnerable to issues of identity mismanagement and exposure to all forms of threats, losses and breach of privacy. Current identity systems have largely failed to deliver any of the most basic requirements for a successful identity system: security, privacy, ownership, access, protection, interoperability, or linked data portability to identity owners. The difficulty presented by centralized platforms in linking data makes the national and international implementation of KYC laws cumbersome to apply. Major services at both local and international levels rely on KYC implementation for execution. In today’s fast-moving world that is driven by technology, transporting huge amounts of data as they are constantly required for these transactions usually lead to delays and other hitches that are responsible for inefficiencies and losses. A Self-Sovereign Identity (SSID) A distributed decentralized ledger such as SelfKey would serve to eliminate the above-mentioned hitches and put users at the centre of the identity management process, a concept known as Self-Sovereign ID, and enables an Identity Ecosystem where users can transfer value among the Participants using a token: “KEY”. The SelfKey token, “KEY” is a cryptocurrency, digital cash, a ERC-20 token which can be freely traded. User’s KEY and identity documents can be stored in their identity wallet, from which they can pay to apply for services (such as a coin exchange account, a new company, or a bank account). The implementation of a decentralized identity management system employs existing blockchain properties to achieve a more secure and effectively managed system that eliminates the ambiguities and insecurities that have besieged the global data management industry. Solving the existing deficiencies Whilst providing tangible utility for the KEY token for identity owners, relying parties and verifiers, through real world products and services, SelfKey overcomes the limitations of centralized identity systems, helps achieve compliance with the most comprehensive national data protection laws and KYC regulations, and returns ownership and control of identity data back to the individual – the identity owner.
The level of control that SelfKey offers users enable them to determine how much of their personal data that they permit or give access to based on particular requests. This simply implies that, rather than companies engaging centralized servers like Facebook and Google to collect data of persons even without their consent, it will be in the power of the identity owners to grant access in bits, based on what they want to permit. Just for functionality However, unlike certain Internet companies, the SelfKey foundation is nonprofit. There is no monetization by way of advertising or sale of user data but minimizing the amount of data which needs to be shared is safer both for the identity provider and the relying party. The identity owner does not share information which might be unnecessary or sensitive data – and the recipient doesn’t need to store it. This helps with both security and compliance with jurisdictional privacy law requirements.